- Office Unit No.1 C.S-2, Neeti Bagh, New Delhi-110049
- contact@feed.net.in
Discover the challenges faced by India’s marginal farmers and explore how FEED is transforming their lives through innovative solutions and strategic partnerships.

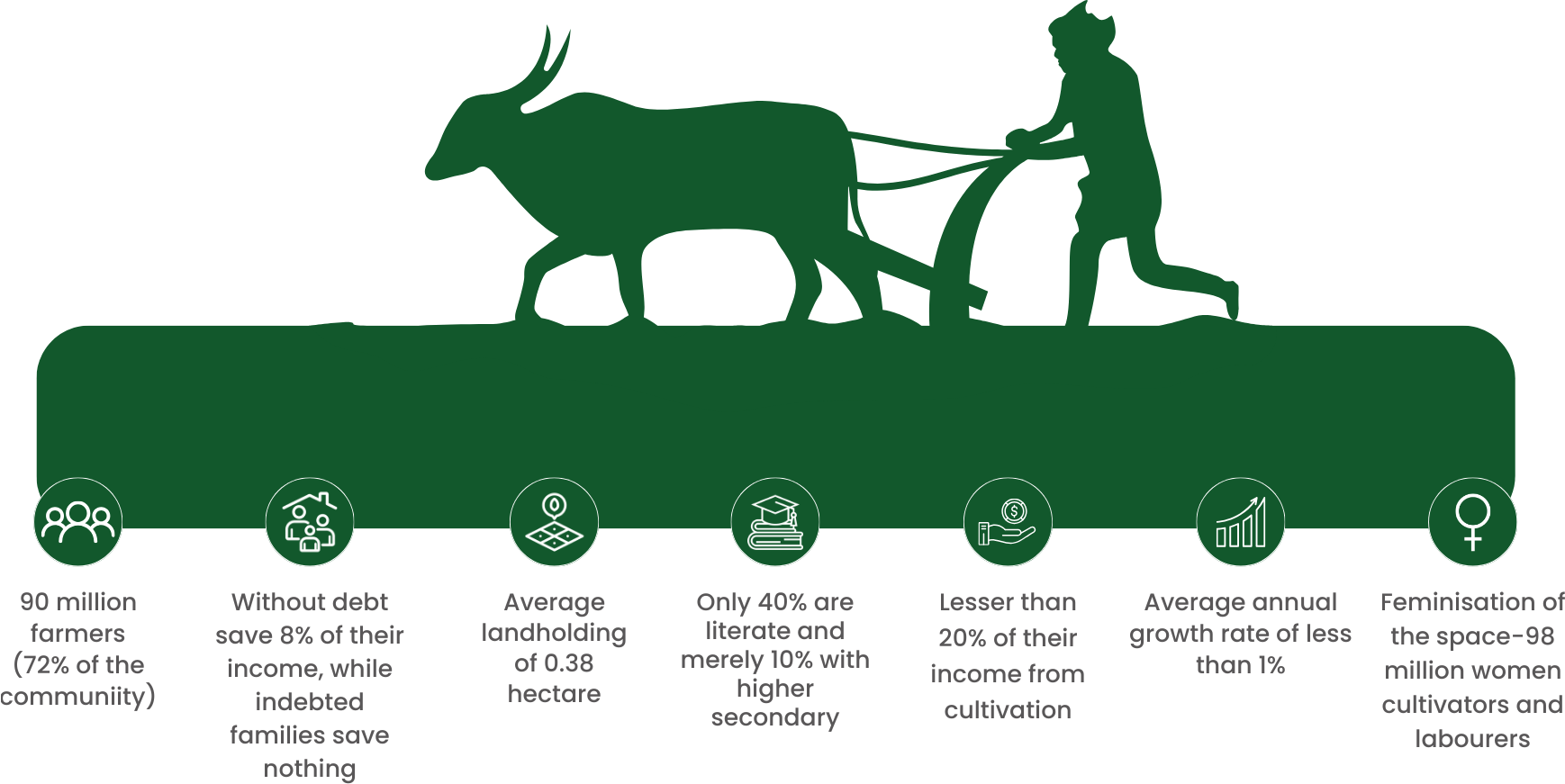
Small land holdings make it difficult for farmers to source essential inputs, including manpower, machinery, and fertilizers, at competitive rates.
Since 2007-08, there has been a sharp increase in the cost of cultivation at an annual rate of 13%, further straining their finances.
An RBI report indicates that 50% of small and marginal farmers are unable to borrow from formal sources due to unclear land titles.
Lengthy loan procedures, demands for collateral, and short-term crop loans force farmers to turn to non-institutional lenders, exacerbating their financial woes.
Farm gate prices have been declining since the mid-2010s.
Rising input costs, high financing costs, and reducing nominal farm incomes make agriculture an increasingly unattractive livelihood option.
Small land holdings make it difficult for farmers to source essential inputs, including manpower, machinery, and fertilizers, at competitive rates.
Since 2007-08, there has been a sharp increase in the cost of cultivation at an annual rate of 13%, further straining their finances.
An RBI report indicates that 50% of small and marginal farmers are unable to borrow from formal sources due to unclear land titles.
Lengthy loan procedures, demands for collateral, and short-term crop loans force farmers to turn to non-institutional lenders, exacerbating their financial woes.
Farm gate prices have been declining since the mid-2010s.
Rising input costs, high financing costs, and reducing nominal farm incomes make agriculture an increasingly unattractive livelihood option.

India has achieved a food surplus, with an all-time high production of food grains in FY19-20 at 320 million tons. However, there remains a significant nutritional deficit of 180 grams per day, primarily due to shortages in fruits, vegetables, milk, and visible fats.
Diversifying the food basket is essential to meet the recommended nutritional needs of the population. Implementing policies and initiatives to promote the production of a variety of food items will help bridge this nutritional gap.


There has been a noticeable shift in employment from rural areas to urban centers, leading to a talent drain that weakens rural economies.
Building resilient rural economies is crucial to retaining talent and preventing the migration of youth to cities.
Private Investments: Increased investments can transform rural centers into industrial hubs.
Public and Private Resources: Development requires a combination of public and private resources for improved farming techniques, technology development, and streamlined supply chains.
Value-Addition Activities: Investments in value-added activities, such as micro warehouses and logistics optimization, are necessary.
Developing programs that suit the economic needs of rural and peri-urban areas is vital for economic growth.
Encouraging youth to acquire skills that enable them to contribute actively to the local economy is crucial.
Creating an ecosystem that supports a new breed of rural entrepreneurs is essential.
Breaking silos in the current agriculture ecosystem is necessary to prevent lost value. FEED aims to bring together all stakeholders under one roof, providing an integrated solution to maximize value.

Current Scenario:
India has achieved a food surplus, with an all-time high production of food grains in FY19-20 at 320 million tons. However, there remains a significant nutritional deficit of 180 grams per day, primarily due to shortages in fruits, vegetables, milk, and visible fats.
Need for Diversification:
Diversifying the food basket is essential to meet the recommended nutritional needs of the population. Implementing policies and initiatives to promote the production of a variety of food items will help bridge this nutritional gap.
Rural Employment Trends:
There has been a noticeable shift in employment from rural areas to urban centers, leading to a talent drain that weakens rural economies.
Resilient Rural Economies:
Building resilient rural economies is crucial to retaining talent and preventing the migration of youth to cities.
Transforming Rural Centers:
Corporate Involvement:
Capacity Building Programs:
Developing programs that suit the economic needs of rural and peri-urban areas is vital for economic growth.
Skill Development:
Encouraging youth to acquire skills that enable them to contribute actively to the local economy is crucial.
Supporting Rural Entrepreneurs:
Creating an ecosystem that supports a new breed of rural entrepreneurs is essential.
Integrated Approach:
Breaking silos in the current agriculture ecosystem is necessary to prevent lost value. FEED aims to bring together all stakeholders under one roof, providing an integrated solution to maximize value.
Integrate farmers into robust value chains to enhance their market reach and improve income.
Develop and strengthen agricultural value chains, establish market linkages to connect farmers with buyers, and promote fair trade practices and transparent transactions.
Provide financial resources to farmers through innovative financing models.
Facilitate access to affordable credit through blended finance models, and partner with financial institutions to offer tailored loan products.
Empower farmers with modern technology to enhance productivity and efficiency.
Introduce advanced farming techniques and tools, train farmers to use technology effectively, and encourage the development of agri-entrepreneurs who leverage tech solutions.
Increase profitability by focusing on high-value crops.
Identify and promote high-value crops suitable for local conditions, provide seeds, training, and support for high-value crop cultivation, and connect farmers with markets that demand high-value produce.
Office Unit No.1 C.S-2, Neeti Bagh, New Delhi-110049
contact@feed.net.in
Get Our Latest Update.